Sleep deprivation is a prevalent issue in today’s fast-paced society, with many individuals sacrificing sleep to meet the demands of work, social obligations, and other responsibilities. However, the impact of sleep deprivation on the brain cannot be underestimated. Extensive research has shown that lack of adequate sleep can have profound effects on cognitive function, memory consolidation, alertness, concentration, decision-making abilities, mood regulation, and overall emotional well-being.
One of the most prominent consequences of sleep deprivation is impaired cognitive function. Studies have consistently demonstrated that individuals who do not obtain sufficient sleep experience difficulties in various cognitive domains such as attention, information processing speed, working memory capacity, and executive functions. These impairments can manifest in everyday tasks such as problem-solving and decision-making processes. Furthermore, memory problems are also commonly observed in individuals suffering from sleep deprivation. The consolidation of newly acquired information into long-term memory relies heavily on quality sleep. Without adequate restorative sleep periods, memories may not be effectively encoded or consolidated into long-term storage areas of the brain. This can result in difficulties with recall and retrieval of information when needed.
In conclusion, understanding the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on brain functioning is crucial for maintaining optimal cognitive performance and overall well-being. By recognizing the impact it has on cognitive function and memory consolidation processes as well as its influence on alertness and decision-making abilities, individuals can prioritize their sleep habits to ensure they obtain enough restorative rest each night. Adopting healthy sleeping habits should be a priority for everyone to safeguard their brain health and maintain optimal cognitive functioning throughout their lives.
Impaired Cognitive Function
Impaired cognitive function is a significant consequence of sleep deprivation, leading to deficits in attention, memory, decision-making, and problem-solving abilities. Sleep plays a crucial role in consolidating memories and facilitating learning processes. When individuals are deprived of adequate sleep, their ability to acquire new information and retain it is compromised. Studies have shown that sleep-deprived individuals exhibit impaired learning capabilities, as they struggle to focus and concentrate on tasks at hand. This can have detrimental effects on academic performance and overall productivity.
Furthermore, decreased productivity is another consequence of impaired cognitive function resulting from sleep deprivation. Lack of sufficient sleep negatively impacts an individual’s ability to perform complex tasks efficiently and effectively. Decision-making becomes more challenging as the brain struggles to process information accurately under conditions of fatigue. Problem-solving abilities are also hindered due to reduced mental flexibility and creativity caused by sleep deprivation. These deficits in cognitive functioning not only affect work-related tasks but also impact daily activities such as driving or operating machinery safely.
Impaired cognitive function resulting from sleep deprivation has far-reaching consequences on various aspects of an individual’s life. The inability to learn effectively and decreased productivity can significantly hinder academic performance and professional success. It is essential for individuals to prioritize adequate sleep in order to maintain optimal cognitive functioning and overall well-being.
Memory Problems
Memory deficits are a common consequence of inadequate sleep. Sleep deprivation has been shown to have a significant impact on various memory processes, leading to memory loss and forgetfulness. One of the main types of memory affected by sleep deprivation is declarative memory, which refers to the ability to recall facts and events. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who are sleep deprived often struggle with encoding new information into their long-term memory, making it difficult for them to remember important details or events.
In addition to impairing the formation of new memories, insufficient sleep also affects memory consolidation. During sleep, the brain consolidates and strengthens memories acquired throughout the day. This process involves transferring memories from short-term storage sites to more permanent regions in the brain. However, when individuals do not get enough sleep, this consolidation process becomes disrupted, leading to difficulties in retaining and retrieving information from long-term memory. Consequently, individuals may experience increased forgetfulness and difficulty recalling previously learned information.
Overall, it is evident that sleep deprivation has detrimental effects on memory function. The impairment of both encoding and consolidation processes contributes to memory deficits characterized by forgetfulness and an inability to retain information effectively. As such, maintaining adequate levels of sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive performance and preserving one’s ability to remember and recall information accurately.
Decreased Alertness
A lack of sufficient sleep significantly diminishes an individual’s level of alertness, leading to reduced cognitive function and potentially compromising their ability to perform daily tasks effectively. Sleep deprivation has been shown to impair attention, concentration, and reaction time, making individuals more prone to accidents and errors. Studies have found that sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to be involved in car accidents or workplace incidents due to their decreased alertness and slower response times.
Furthermore, decreased productivity is another consequence of sleep deprivation. When individuals are sleep deprived, they experience difficulties in focusing on tasks and maintaining sustained attention. This can lead to reduced efficiency in completing work assignments or academic tasks. Additionally, the impaired cognitive function resulting from sleep deprivation hampers problem-solving abilities and creative thinking. As a result, individuals may struggle with decision-making processes and find it challenging to generate innovative ideas.
The impact of sleep deprivation on alertness is profound. It not only increases the risk of accidents but also decreases productivity by impairing cognitive function. Recognizing the importance of adequate sleep for optimal brain performance is crucial in ensuring individuals’ well-being and maximizing their potential in various aspects of life.
Difficulties in Concentration
Difficulties in concentration can significantly impact an individual’s ability to focus on tasks and maintain sustained attention. Sleep deprivation has been shown to have a detrimental effect on attention span and mental focus. When sleep deprived, the brain’s ability to concentrate becomes impaired, leading to decreased productivity and performance.
One of the key consequences of sleep deprivation is a shortened attention span. Research has found that individuals who are sleep deprived tend to have a reduced ability to sustain their attention on a particular task or activity for extended periods of time. This can manifest as increased distractibility, difficulty staying focused, and a tendency to make more errors. The lack of sufficient restorative sleep negatively affects the brain’s cognitive functions, making it harder for individuals to filter out distractions and stay engaged in tasks that require mental effort.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation also impairs mental focus. It becomes more challenging for individuals who are sleep deprived to concentrate on complex or demanding tasks that require cognitive processing and problem-solving skills. The tired brain is less able to process information efficiently, leading to difficulties in decision-making and critical thinking. Moreover, studies have shown that sleep-deprived individuals may experience slower reaction times and decreased accuracy when performing mentally demanding tasks.
Difficulties in concentration are a significant consequence of sleep deprivation. The compromised attention span and impaired mental focus can greatly hinder an individual’s ability to perform effectively in various aspects of life, including work or academic pursuits. Recognizing the importance of adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal cognitive functioning and overall well-being.
Impact on Decision Making
Impaired cognitive functioning due to inadequate sleep can significantly impact an individual’s ability to make sound decisions and engage in effective problem-solving. Sleep deprivation has been shown to impair judgment, leading to a reduced ability to assess risks accurately. Studies have demonstrated that individuals who are sleep deprived tend to exhibit increased risk-taking behavior, making impulsive decisions without properly evaluating the potential consequences.
Research has revealed that sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to engage in risky activities such as driving under the influence or participating in dangerous sports. This impaired judgment can also extend beyond immediate risks and affect long-term decision-making processes. For example, individuals who lack sufficient sleep may struggle with financial decision-making, opting for short-term gains rather than considering long-term investments or savings.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can hinder the ability to think critically and solve problems effectively. When faced with complex situations, individuals who are sleep deprived may struggle with logical reasoning and fail to consider all relevant factors before making a decision. This compromised cognitive functioning not only impairs individual performance but also extends its impact on professional settings where critical thinking is essential.
Inadequate sleep negatively affects decision-making abilities by impairing judgment and increasing risk-taking behavior. The consequences of impaired cognitive functioning extend beyond immediate risks and can detrimentally impact long-term decision-making processes as well. It is therefore crucial for individuals to prioritize sufficient sleep in order to maintain optimal brain function and make sound decisions.
Information Retention Challenges
Challenges arise in retaining information when one’s cognitive functioning is compromised due to inadequate sleep. Sleep deprivation has been shown to have a negative impact on learning and academic performance. When individuals do not get enough sleep, their ability to acquire new information and consolidate memories becomes impaired. This can make it difficult for them to retain and recall important information.
Research has consistently demonstrated the connection between sleep deprivation and learning difficulties. Lack of sleep affects various cognitive processes that are crucial for effective learning, such as attention, concentration, and problem-solving skills. These impairments can lead to decreased motivation and engagement in academic tasks, resulting in lower academic performance.
Furthermore, inadequate sleep negatively influences memory consolidation. During deep sleep stages, the brain strengthens connections between neurons involved in forming memories, allowing for better retention of learned material. However, when individuals are deprived of sufficient sleep, this process is disrupted, leading to difficulties in retaining information.
Overall, insufficient sleep compromises cognitive functioning necessary for effective learning and memory consolidation. The impact of sleep deprivation on information retention highlights the importance of prioritizing adequate sleep for optimal academic performance.
Mood and Emotional Well-being
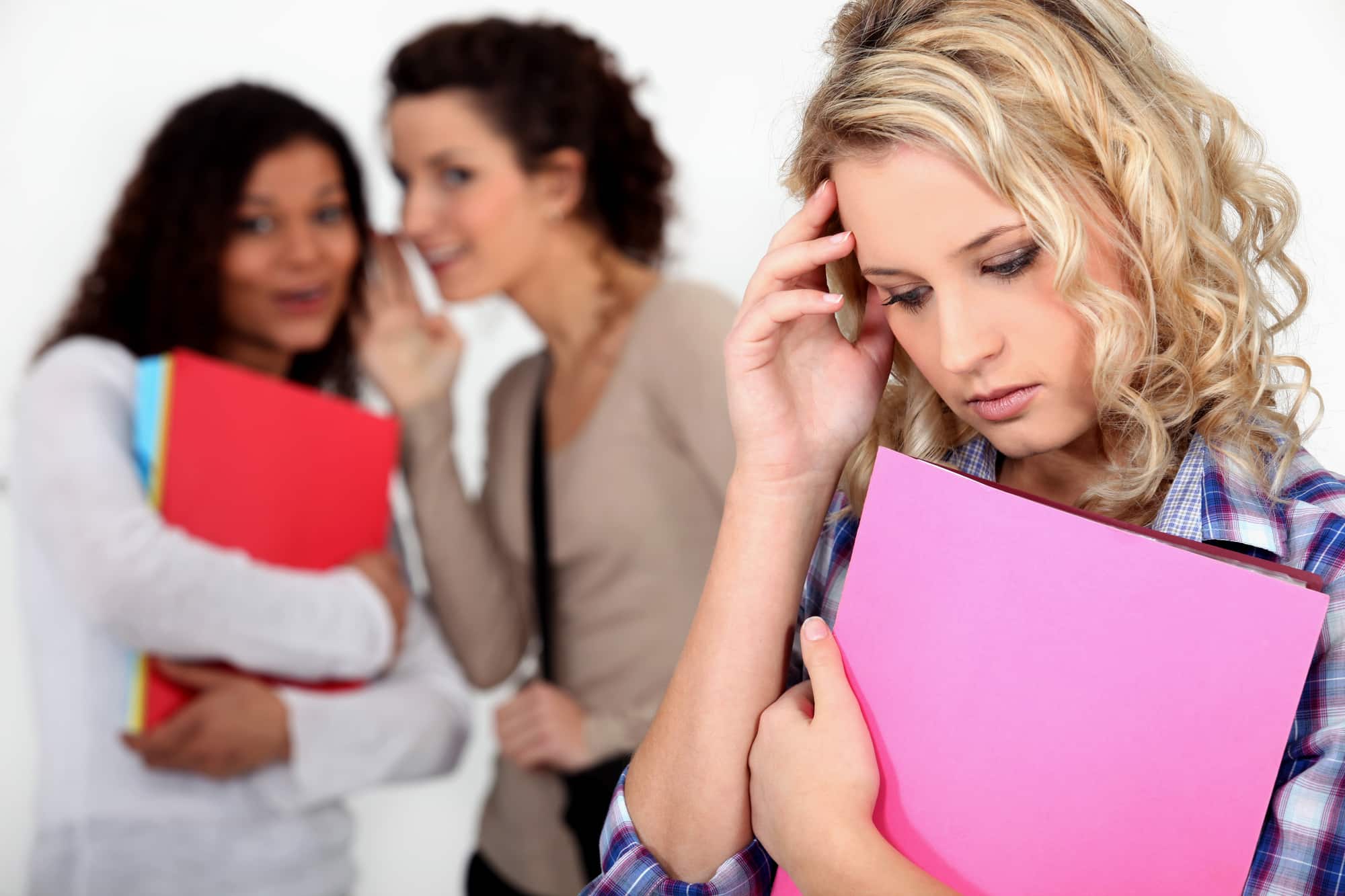

The impact of inadequate sleep on information retention extends beyond cognitive functioning, as it also affects one’s mood and emotional well-being. Sleep deprivation has been found to disrupt emotional regulation, leading to an increase in negative emotions and a decrease in positive emotions. Studies have shown that individuals who don’t get enough sleep are more likely to experience irritability, anger, and sadness. They may also have difficulty managing stress and regulating their emotions effectively.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on psychological health. Lack of sleep has been associated with an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. It is believed that the disruption of the brain’s normal functioning due to sleep loss contributes to these psychological challenges. Additionally, individuals with chronic insomnia or other sleep disorders often report higher levels of stress and lower overall life satisfaction.
Overall, the effects of inadequate sleep extend beyond mere cognitive functioning. Sleep deprivation can negatively impact emotional regulation and contribute to psychological health issues such as depression and anxiety. Prioritizing sufficient quality sleep is essential for maintaining optimal mood and emotional well-being.
Irritability and Mood Swings
Sleep deprivation not only affects mood and emotional well-being but also manifests in increased irritability and mood swings. When individuals do not get enough sleep, they may find themselves more easily irritated by minor inconveniences or frustrated by daily challenges. This heightened sensitivity is often a result of decreased emotional regulation capabilities, which can affect how one processes and reacts to various situations.
Managing irritability caused by sleep deprivation involves implementing strategies to improve overall sleep quality and quantity. One approach is maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate the body’s internal clock and promotes better sleep patterns. Additionally, creating a conducive sleeping environment free from distractions such as noise or excessive light can aid in achieving restful sleep.
Emotional regulation techniques are also beneficial for managing irritability associated with sleep deprivation. These methods involve recognizing and acknowledging emotions without judgment while actively seeking ways to calm oneself down. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as deep breathing exercises or mindfulness meditation, can help individuals regain control over their emotions when faced with irritability or mood swings due to lack of sleep. Furthermore, incorporating regular physical exercise into daily routines has been shown to have positive effects on both sleep quality and emotional well-being.
Inadequate sleep can lead to increased irritability and mood swings due to impaired emotional regulation. By prioritizing sufficient rest through consistent sleeping habits and utilizing effective emotional regulation techniques, individuals can minimize the negative impact of sleep deprivation on their mood and overall well-being.
Negative Outlook on Life
A persistent lack of sufficient sleep can lead to a pessimistic outlook on life, affecting one’s overall perspective and attitude. When individuals consistently experience sleep deprivation, their ability to maintain a positive mindset becomes compromised. Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating emotions and enhancing emotional resilience. Without adequate rest, individuals may find it challenging to remain optimistic and may struggle with managing negative thoughts and feelings.
Research has shown that sleep deprivation can impair the brain’s ability to process positive information effectively. This cognitive bias towards negativity can result in a heightened focus on negative aspects of life while minimizing or overlooking positive experiences. As a result, individuals experiencing sleep deprivation may perceive situations more negatively than they would under normal circumstances.
Furthermore, insufficient sleep affects emotional resilience, which refers to an individual’s capacity to adapt and cope with stressors effectively. Sleep-deprived individuals tend to have reduced emotional resilience, making them more susceptible to feelings of irritability, frustration, and sadness. This diminished emotional resilience further contributes to their negative outlook on life as they find it difficult to bounce back from setbacks or find silver linings in challenging situations.
Chronic sleep deprivation can significantly impact an individual’s perspective on life by diminishing their ability to maintain a positive mindset and emotional resilience. It is essential for individuals to prioritize adequate sleep as part of their overall well-being in order to foster a more optimistic outlook on life and enhance their overall mental health.
Prioritizing and Improving Sleep Habits
To optimize one’s overall well-being and cultivate a more positive mindset, it is crucial to prioritize and enhance the quality of sleep habits. This can be achieved through practicing good sleep hygiene and ensuring adequate sleep duration. Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices and behaviors that promote healthy sleep patterns. It includes maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleeping environment, limiting exposure to stimulating activities before bedtime, avoiding caffeine and alcohol intake close to bedtime, and engaging in relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing exercises. By adhering to these practices, individuals can establish a regular sleep routine that allows their body and mind to relax and prepare for restful slumber.
In addition to maintaining good sleep hygiene, improving the quality of sleep is equally important. Sleep quality refers to how well an individual sleeps during the night and how refreshed they feel upon waking up. Achieving high-quality sleep involves several factors such as having uninterrupted periods of deep sleep, experiencing minimal awakenings throughout the night, and reaching the necessary amount of REM (rapid eye movement) sleep cycles. To enhance sleep quality, individuals can engage in activities that promote relaxation before bed like reading a book or taking a warm bath. Creating a calm bedroom environment with dim lighting and comfortable bedding can also contribute to better sleep quality. Moreover, establishing a regular exercise routine during the day has been shown to improve both the duration and quality of sleep.
By prioritizing these aspects of sleep habits – namely adhering to good sleep hygiene practices and improving overall sleep quality – individuals can greatly influence their brain function positively. Adequate high-quality rest provides the brain with an opportunity for restoration by allowing it time for memory consolidation processes, emotional regulation mechanisms, cognitive functioning improvement, as well as neural repair processes that occur during deep stages of non-REM (NREM) or slow-wave-sleep (SWS). Therefore, investing in healthy sleeping habits should not be underestimated as it plays an integral role in maintaining optimal brain health and overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleep deprivation has a significant impact on the brain’s cognitive function. It impairs memory and decreases alertness, making it difficult to concentrate and make decisions effectively. Moreover, sleep deprivation can negatively affect mood and emotional well-being, leading to irritability, mood swings, and a negative outlook on life.
To mitigate the detrimental effects of sleep deprivation on the brain, it is crucial to prioritize and improve sleep habits. By ensuring an adequate amount of quality sleep each night, individuals can enhance their cognitive abilities, memory retention, alertness levels, concentration skills, and decision-making capabilities. Additionally, adopting healthy sleep habits can contribute to improved mood and emotional well-being by reducing irritability and promoting a more positive outlook on life.
Overall, recognizing the importance of sufficient sleep and taking proactive steps towards maintaining good sleeping habits is essential for optimizing brain function and overall well-being.